
ICMR Project
The primary purpose of hospital-based Cancer registries is to contribute to patient care by providing readily accessible information on patients with cancer, the treatment received, and its results.
Under the NCRP (National Cancer Registry Programme), MTMH has set up a Hospital Based Cancer Registry (HBCR) for the period 2017-2022.
Cancer Information
MTMH is proud to be associated with the Jeet Association for Support to Cancer Care (JASCAP), an NGO dedicated to providing patient information on cancer care. This is the fourth oncology centre of TATA for JASCAP – there are two in Mumbai, one in Kolkata and now in Jamshedpur. This association between JASCAP and MTMH is sure to empower patients and their caregiver community immensely.
Click here to read about JASCAP and to know more about the association with MTMH.

What is Cancer?
There are several major types of cancers:
- Carcinomas form in the cells that cover the skin or line the mouth, throat, lungs, and organs
- Sarcomas are found in the bones, muscles, fibrous tissues, and some organs
- Leukaemia is found in the blood, the bone marrow, and the spleen
- Lymphomas are found in the lymphatic system
Causes of Cancer
Cancer often takes many years to develop. The process typically begins with some disruption to the DNA of a cell, the genetic code that directs the life of the cell.
There can be many reasons for disruptions to the DNA of a cell. These are a few common ones
- Diet
- Tobacco
- Sun exposure
- Reproductive history
- Certain chemicals
Some cells will enter a precancerous phase, known as dysplasia. Some cells will progress further to the state of carcinoma in situ, in which the cancer cells are restricted to a microscopic site, surrounded by a thick covering, and do not pose a great threat.
Eventually, unless the body’s immune system takes care of the wayward cells, a cancer will develop. It may take as long as 30 years for a tumour to go through the entire process and become large enough to produce symptoms.

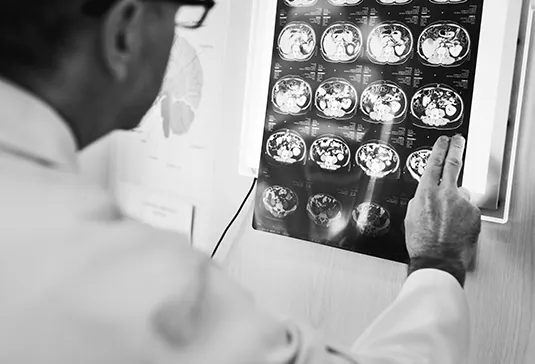
Symptoms of Cancer
Since cancer can arise from such a wide variety of sites and develop with many differing patterns of spread, there are no clear- cut symptoms. The precise nature of symptoms of cancer depends not only on the primary site but specifically on where the tumour is located in an organ, the rate of development and if the secondary spread is present or not.
Many primary tumours cause local swelling or lump if they arise at a visible or accessible part of the body, such as the skin, breast, testicle, or oral cavity. A typical swelling due to cancer is initially painless, though ulceration (skin breakdown) can occur, which may then become painful.
Treatment of Cancer
The aim of cancer treatment is to cure the patient and save their life. In cases where a complete cure is not possible, treatment aims to control the disease and to keep the patient normal and comfortable for as long as possible. The treatment of each patient is designed to suit the patient based on three parameters
- Age of the patient
- Stage of the disease
- Type of the disease
Treatment through surgery
Treatment through radiotherapy
Radiotherapy has become the pre-eminent form of cancer treatment since the beginning of this century and now it is used for fifty percent of patients. Improvements in radiotherapy equipment, technique, and applications, have led to an increasing role both in local treatment and in its use as a whole-body treatment, as part of bone marrow transplantation techniques for leukaemia and other malignant diseases.
Radiation is a special kind of energy carried by waves or a stream of particles originating from radioactive substances and delivered by special machines. These radioactive X-rays or gamma rays can penetrate the cell wall and damage the nucleus of the cell which prevents the growth and division of cells. This also affects the normal cells but these cells recover more fully than cancer cells.
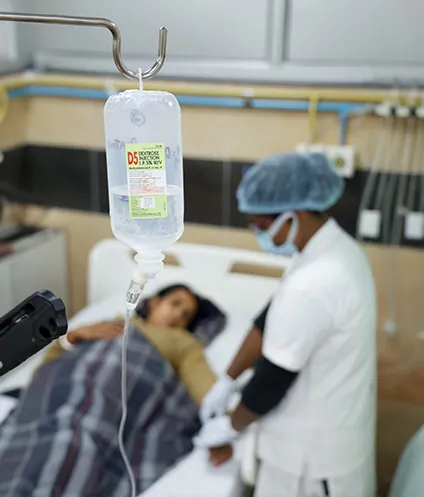
Chemotherapy uses drugs which interfere with the growth and division of malignant cells. Once the drugs are administered, they circulate throughout the body. It is advantageous over surgery and radiation for treating cancer that is systemic (spread throughout the body). Chemotherapy is very useful in treating cancers like leukaemia, lymphomas, and testicular cancer. Chemotherapy can be given as the primary treatment, or following surgery or radiotherapy to prevent the reappearance of cancer.
The side effects of the chemotherapy include nausea, vomiting, hair loss, fever etc. which are temporary and completely reversible.
Treatment through chemotherapy
Treatment through hormone therapy
- Bladder Cancer
- Cervical Cancer
- Colorectal Cancer
- Gastric (Stomach Cancer)
- Head and Neck Cancer
- Leukaemia
- Lung Cancer
- Skin Cancer
- Radiation Therapy
- Medical Oncology
- Surgical Oncology
